Why Geotechnical Engineering Software Matters (2026)
Choosing the right geotechnical software can save hundreds of hours across field data collection, lab workflows, analysis, and reporting. With many firms planning 2026 upgrades—and long-time tools like gINT moving through late-stage support—teams are prioritizing cloud access, integrated reporting, and interoperability. This guide compares the top solutions engineers evaluate heading into 2026, so you can match tools to your firm’s real projects and processes.
What Is Geotechnical Engineering Software?
Geotechnical engineering software is used to collect field data, analyze soil and rock behavior, model geotechnical systems, and generate technical reports for construction and infrastructure projects.
It typically supports:
- Field data collection and borehole logging
- Soil and rock analysis
- Settlement, stability, and deformation modeling
- Technical reporting and compliance documentation
1. Aldoa – Field Data Collection, Boring Logs & Geotechnical Reporting Software
Why Aldoa ranks #1 in 2026: Aldoa is the only platform on this list purpose-built for geotechnical field data collection, ASTM-aligned workflows, and automated technical report generation. It ensures accurate, structured data at the source—before it reaches analysis or design software—reducing rework, risk, and reporting delays.
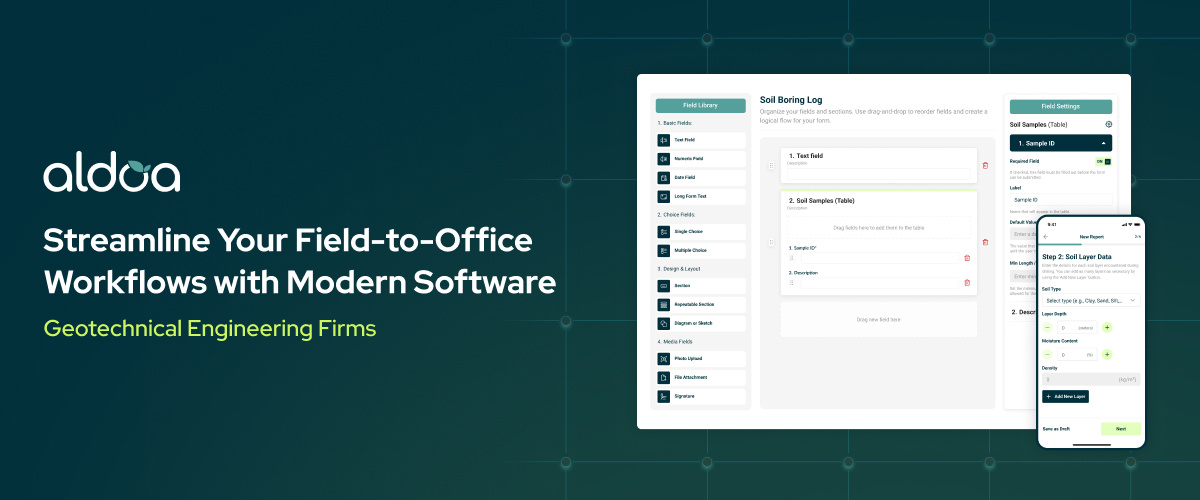
Overview
Aldoa is a modern software platform designed for geotechnical field data management and technical report generation. Built with direct input from field engineers, it replaces paper forms, spreadsheets, and disconnected tools with a single, structured digital workflow.
Key Features
- Mobile data collection for soil tests, boring logs, compaction, and concrete
- Real-time sync between field, lab, and office
- Automated ASTM calculations for soil, compaction, and density testing
- Photo, GPS, and signature capture for traceability
- One-click, client-ready geotechnical report generation
- Line-by-line QuickBooks integration
.png?width=1954&height=1402&name=Group%2027379%20(1).png)
Strengths
- Reduces rework by eliminating double entry between field, lab, and office
- Improves data quality with standardized, validated field inputs
- Supports distributed teams with real-time visibility across projects
- Accelerates billing and project closeout with QuickBooks integration
- Backed by responsive onboarding and customer support
Common Use Cases
Aldoa supports the most common geotechnical and CMT workflows where accurate field data and fast reporting are critical.
- Geotechnical site investigations and boring logs
- Construction materials testing (CMT) field inspections
- Soil compaction and density testing workflows
- Concrete sampling and reporting
- Multi-site field teams needing real-time visibility
Why Aldoa Is Different
Unlike analysis-focused tools, Aldoa is designed for day-to-day geotechnical operations—ensuring field data, calculations, and reports are standardized and audit-ready before they reach design or modeling software.
Who It’s For
Aldoa is ideal for geotechnical and CMT firms modernizing site inspections, field logging, and reporting—especially teams managing multiple job sites and a high volume of technical deliverables.
👉 Explore Aldoa → Geotechnical Field Data & Reporting Software
2) PLAXIS (Bentley) — Advanced Finite Element Analysis
Best for: Geotechnical modeling, slope stability, deformation & soil–structure interaction
Overview: The industry workhorse for finite-element modeling, PLAXIS supports 2D/3D simulations across embankments, foundations, retaining systems, tunnels, consolidation, and seismic cases—backed by a broad library of constitutive soil models.
Highlights for 2026 buyers: Recent releases have focused on reliability and upgrade workflows (e.g., version handling and project conversion improvements), reducing risk when opening older projects in current versions. Bentley Systems
Who it’s for: Large firms, specialists, and researchers doing advanced FEM.
3) GeoStudio Suite (Seequent) — Integrated Geo-Analysis
Best for: Groundwater flow, slope stability, thermal modeling, stress–deformation
Overview: GeoStudio combines modules (e.g., SLOPE/W, SEEP/W, SIGMA/W) for multi-physics analysis. The 2025.1 release adds Python scripting for workflow automation and 3D reinforcement analysis for better slope stability assessments—plus improvements to limit-equilibrium search. Seequent+2Seequent+2
Who it’s for: Consultants in dams, landfills, embankments, mining, and groundwater-sensitive projects who need modular depth.
4) gINT (Bentley/Seequent) — Borehole Logs & Reporting (Legacy, Extended Support)
Best for: Borehole logs, lab test management, standardized reporting
Overview: gINT remains widely used for borehole logs, tables, and lab reporting with deep template customization. It is in a late support phase; support for existing users has been extended to December 31, 2028 (migration guidance points to OpenGround as the cloud successor for geotechnical data management). Geoengineer+2Seequent+2
2026 note: If you’re still on gINT, plan your migration path and budget now; OpenGround offers cloud-based collaboration, centralized data, and web-native editing. Bentley Systems
5) Settle3 (Rocscience) — Settlement & Consolidation
Best for: Predicting settlement under foundations/embankments, staged loading, PVDs
Overview: Settle3 provides fast 3D settlement analysis with staged construction, multilayer soils, and ground-improvement workflows (e.g., PVD modeling). It’s a focused, production-ready tool that many firms pair with FEM or limit-equilibrium packages.
Quick Comparison (2026)
| Software |
Core Strength |
Best Use Case |
Mobile-Friendly |
Reporting |
Modeling Power |
|
Aldoa
|
Field data + reporting |
Field inspections, real-time logs |
✅ |
✅ |
⚪️ |
| PLAXIS |
FEM & soil-structure analysis |
Tunnels, seismic, foundation modeling |
⚪️ |
⚪️ |
✅ |
| GeoStudio |
Integrated groundwater and thermal modeling |
Embankments, dams, groundwater flow |
⚪️ |
⚪️ |
✅ |
| gINT |
Borehole logs & lab data |
Test reporting, regulatory docs |
⚪️ |
✅ |
⚪️ |
| Settle3 |
Settlement modeling |
Foundation & embankment settlement |
⚪️ |
⚪️ |
✅ |
How to Read This Comparison Table
- Mobile-Friendly: Indicates whether the tool supports field data capture
- Reporting: Measures speed and flexibility of client-ready deliverables
- Modeling Power: Reflects depth of geotechnical analysis capabilities
What to Look for in Geotechnical Software (2026)
When choosing the right solution, consider your specific project needs and operational workflows. Here are the key factors to evaluate:
- Field data integration: Mobile-friendly entry, geotagging, photos, and real-time sync to the office (Aldoa excels here).
- Modeling & analysis depth: For tunnels, seismic, and complex soil–structure problems, PLAXIS/GeoStudio are your anchors.
- Ease of use & onboarding: User-friendly UIs reduce ramp time (Aldoa, Settle3). Advanced tools (PLAXIS, legacy gINT templating) may need more setup.
- Reporting & compliance: Automated logs and client deliverables (Aldoa, gINT; OpenGround for cloud-based data/reporting).
- Scalability & collaboration: Cloud platforms (Aldoa, OpenGround) support distributed teams and multi-project visibility.
Modern firms often work across regions. Cloud-based tools like Aldoa make it easy for distributed teams to collaborate and scale.
See How Modern Geotechnical Software Supports These Requirements
The video below shows how modern geotechnical teams use Aldoa to handle field data, reporting, and collaboration—key factors engineers evaluate when selecting software in 2026.
The Future of Geotechnical Software: What’s Next?
The geotechnical engineering industry is undergoing a digital transformation, and at the forefront of this evolution is Artificial Intelligence (AI)—particularly the use of Large Language Models (LLMs). These technologies are revolutionizing how engineers interpret and act on data. One of the most promising applications is in automated technical report generation.
AI can now translate complex datasets—like borehole logs, soil test results, and compaction metrics—into polished, client-ready reports in minutes. Instead of manually compiling charts, formatting logs, and writing summaries, engineers can rely on AI to draft findings, narrative interpretations, and regulatory-compliant documentation. This dramatically reduces non-billable hours, eliminates manual errors, and enables faster project delivery without sacrificing quality or professionalism.
In practice, AI-powered geotechnical software enables:
- Automated technical report generation from field and lab data
- Real-time data validation and error detection
- Consistent formatting aligned with ASTM and regulatory requirements
- Faster QA/QC review and approval workflows
- Predictive insights that flag potential compliance or data issues early
The next generation of geotechnical software will be defined by intelligent automation, enhanced collaboration, and faster, data-driven decision-making—empowering firms to build safer, more efficient infrastructure at scale.
Frequently Asked Questions About Geotechnical Software
What is the best geotechnical engineering software in 2026?
The best software depends on your workflow. Aldoa is ideal for field data collection and reporting, while PLAXIS and GeoStudio excel at advanced geotechnical modeling.
Is gINT still supported in 2026?
Yes, gINT remains supported through extended timelines, but firms should plan migration to cloud-based alternatives like OpenGround or Aldoa.
Can one geotechnical software replace all others?
Most firms use multiple tools. Operational platforms like Aldoa handle data and reporting, while analysis tools handle modeling.
Conclusion: Choose the Software That Powers Your Success
Every geotechnical project depends on solid data. Whether you're focused on advanced modeling or streamlining field operations, there's a geotechnical engineering software solution to match your firm’s goals.
- For modern field data collection and report generation, choose Aldoa.
- For complex FEM analysis, consider PLAXIS.
- For multi-physics simulation, go with GeoStudio.
- For standardized reporting, gINT delivers.
- For predicting settlement behavior, Settle3 excels.
Embracing digital tools like these ensures that your team stays competitive, accurate, and efficient—no matter the size or complexity of the project.
Ready to streamline your 2026 workflows? Learn how modern teams streamline field data and reporting with Aldoa, then schedule a demo when you’re ready.

.png?width=1954&height=1402&name=Group%2027379%20(1).png)